Everyone loves the smell of freshly baked bread. So tempting that you want to cut a slice right away. But where does …
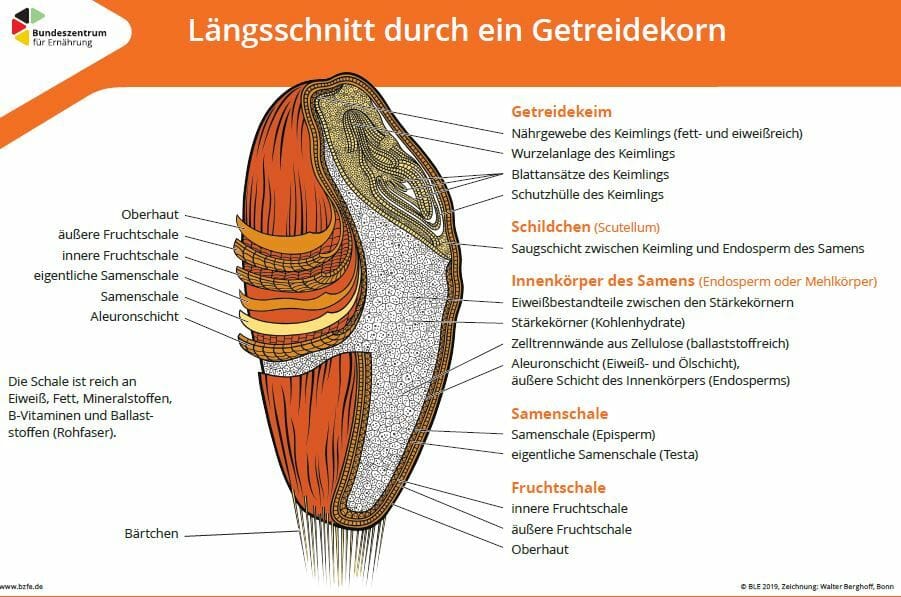
Structure of a grain
The cereal grain is rich in ingredients, most of which are essential for our body. It includes carbohydrates, proteins and fats – the three macronutrients. In addition, cereals contain both micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and secondary plant compounds. In today’s article you will learn which nutrients are found in which part of the grain.
In general, a cereal grain consists of
The endosperm, also called the endosperm, is the largest part of the grain in terms of quantity and weight. It is composed of starch bodies with adhesive proteins between them and delineated by fiber-rich[3] cell partitions. The entire endosperm is surrounded by the so-called aleurone layer. This is composed of proteins and oils and is rich in B vitamins, as well as vitamin E. The endosperm is an energy store that nourishes the germ – especially when it germinates.
“The germ and marginal layers are rich in vitamins and minerals, they contain fatty acids, including essential linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids, and high-quality protein.” [4] The marginal layers protect the grain – but especially the germ. This is also the reason why they are very rich in fiber.
We have summarized for you which vitamins are found in cereals.
In another blog post.
summarized for you. And also to the
secondary plant substances
you will find interesting information on our blog. Have fun reading!
[1] Rittenau, N. (2019): Goodbye vegan cliché! Scientific answers to critical questions about vegan nutrition. Mainz: Ventil Verlag UG & Co. KG, p. 238
[2] Rittenau, N. (2019): P. 238; Münzing-Ruef, I. (2000): Course book healthy eating. The kitchen as nature’s pharmacy. Munich: Wilhelm Heyne Verlag, p. 301; Koerber, K., Männle, T., Leitzmann, C. (2004): Whole food nutrition : conception of a contemporary and sustainable diet. Stuttgart: Haug, p. 244
[3] What dietary fiber is and how it works in the body, you can read in
learn about this post >>
[4] Koerber, K., Männle, T., Leitzmann, C. (2004): S. 244
Figure: https://www.ble-medienservice.de/frontend/esddownload/index/id/304/on/6207/act/dl (10.03.2020)
Everyone loves the smell of freshly baked bread. So tempting that you want to cut a slice right away. But where does …
What is the difference? White flour:When the bran, i.e. the marginal layers, and the valuable germ are removed from the grain, we …
Hello and greetings! Also in the life of a mouse it is important to be always up to date and well informed. …
When it comes to eating breakfast, each of us has our own habits, certain preferences or maybe even skips the morning meal …
Address:
Gasteigweg 25,
5400 Hallein
Austria
Opening hours:
Monday to Thursday: 09 – 16:00
Friday: 09 – 12:00
Contact:
Phone: +43 6245 83282
E-Mail:
info@agrisan.at



